

Follow instructions for moving your arm and doing exercises to keep your arm strong.It may help to use a pillow to support your elbow while sitting. Your doctor may advise you to keep your arm next to your body. Occasionally bleeding (open fracture) Loss of normal use of the arm if a nerve injury occurs A humerus shaft fracture may be treated with or without surgery, depending on the fracture pattern and associated injuries (i.e., nerve injury or open fracture).If you are not taking a prescription pain medicine, ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter medicine.
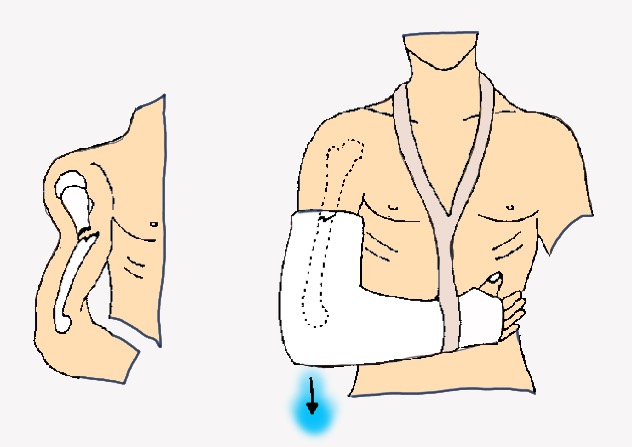
 If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed. If you have a sling, do not take it off unless your doctor tells you to. Follow the care instructions your doctor gives you. Untreated fractures can lead to hypovolaemic shock especially if open, and should be treated with effective haemorrhage control and splintage. If you do not have a splint or cast, use a cloth between the ice and your skin. Lower limb fractures are common injuries in prehospital care. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your cast or splint. Try to do this every 1 to 2 hours for the next 3 days (when you are awake). It also helps to decrease pain and improve. The brace looks like a clamshell and holds the humerus in alignment. Put ice or a cold pack on your arm for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. A coaptation splint is a splinting technique used to support and protect the upper arm or humerus fractures. Usually, the fracture is treated in a splint or sling for a week to allow swelling to subside, and then youre fitted with a fracture brace. If the splint is too tight, it can lead to compartment syndrome, without devastating consequences. A swathe is another immobilization option that provides extra support and further reduces movement by. Patient monitoring after splint placement is recommended. Wearing a sling provides arm support and immobilization. An interprofessional team consisting of emergency physicians, orthopedists, and emergency or orthopedic nurses will improve care and outcomes. Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs. The practitioner needs to take time to become familiar with the materials and techniques needed to make a well-padded and molded splint that properly positions a patient to maintain a reduction and allow for soft tissue swelling. Supracondylar Fractures are one of the most common traumatic fractures seen in children and most commonly occur in children 5-7 years of age from a fall on an outstretched hand. It typically is removed, and patients are transitioned into more definitive immobilization such as a cast. Cast padding is wrapped around the upper arm, elbow, forearm and hand, as far as the transverse flexor crease of the palm (the MP joints are left free). Typically, a long arm splint is the initial form of immobilization. This form of splinting can provide excellent immobilization while allowing for swelling that often accompanies acute injuries. Some people only need a splint or cast for the bone to heal. You might need surgery to repair your bone. Long arm splints are a valuable tool in the treatment of a variety of upper extremity injuries. Transverse fractures are almost always caused by traumas like falls or car accidents. Long arm splints may be applied by many healthcare workers including therapists and orthopedic nurses.
If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed. If you have a sling, do not take it off unless your doctor tells you to. Follow the care instructions your doctor gives you. Untreated fractures can lead to hypovolaemic shock especially if open, and should be treated with effective haemorrhage control and splintage. If you do not have a splint or cast, use a cloth between the ice and your skin. Lower limb fractures are common injuries in prehospital care. Put a thin cloth between the ice and your cast or splint. Try to do this every 1 to 2 hours for the next 3 days (when you are awake). It also helps to decrease pain and improve. The brace looks like a clamshell and holds the humerus in alignment. Put ice or a cold pack on your arm for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. A coaptation splint is a splinting technique used to support and protect the upper arm or humerus fractures. Usually, the fracture is treated in a splint or sling for a week to allow swelling to subside, and then youre fitted with a fracture brace. If the splint is too tight, it can lead to compartment syndrome, without devastating consequences. A swathe is another immobilization option that provides extra support and further reduces movement by. Patient monitoring after splint placement is recommended. Wearing a sling provides arm support and immobilization. An interprofessional team consisting of emergency physicians, orthopedists, and emergency or orthopedic nurses will improve care and outcomes. Diagnosis can be made with plain radiographs. The practitioner needs to take time to become familiar with the materials and techniques needed to make a well-padded and molded splint that properly positions a patient to maintain a reduction and allow for soft tissue swelling. Supracondylar Fractures are one of the most common traumatic fractures seen in children and most commonly occur in children 5-7 years of age from a fall on an outstretched hand. It typically is removed, and patients are transitioned into more definitive immobilization such as a cast. Cast padding is wrapped around the upper arm, elbow, forearm and hand, as far as the transverse flexor crease of the palm (the MP joints are left free). Typically, a long arm splint is the initial form of immobilization. This form of splinting can provide excellent immobilization while allowing for swelling that often accompanies acute injuries. Some people only need a splint or cast for the bone to heal. You might need surgery to repair your bone. Long arm splints are a valuable tool in the treatment of a variety of upper extremity injuries. Transverse fractures are almost always caused by traumas like falls or car accidents. Long arm splints may be applied by many healthcare workers including therapists and orthopedic nurses. 
To achieve this, anatomy, which is more cone-like than cylindrical (e.g., forearm), may require interrupting wraps rather than continuous circumferential layers.
Also of note, it is important to lay on web roll with 50% overlap to maintain even padding without irregularities, which can be a source of irritation. Web roll should be extended proximally, often to the proximal one-third of the humerus. Frequently, the practitioner can tear pieces of web roll to lay on the posterior aspect of the elbow to provide padding without overbulking the antecubital fossa. At the elbow, web roll must be carefully applied to ensure adequate padding of the olecranon.
#Splinting humerus fracture for free
Care should be taken to accurately define the distal borders of the splint to allow for free motion of the thumb and metacarpal phalangeal joints. The number of layers is determined by the amount of expected swelling, but many splints will use two to four layers. With the patient adequately positioned, start building the splint, unrolling the web roll at the wrist, and extending past the elbow to the upper arm.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
